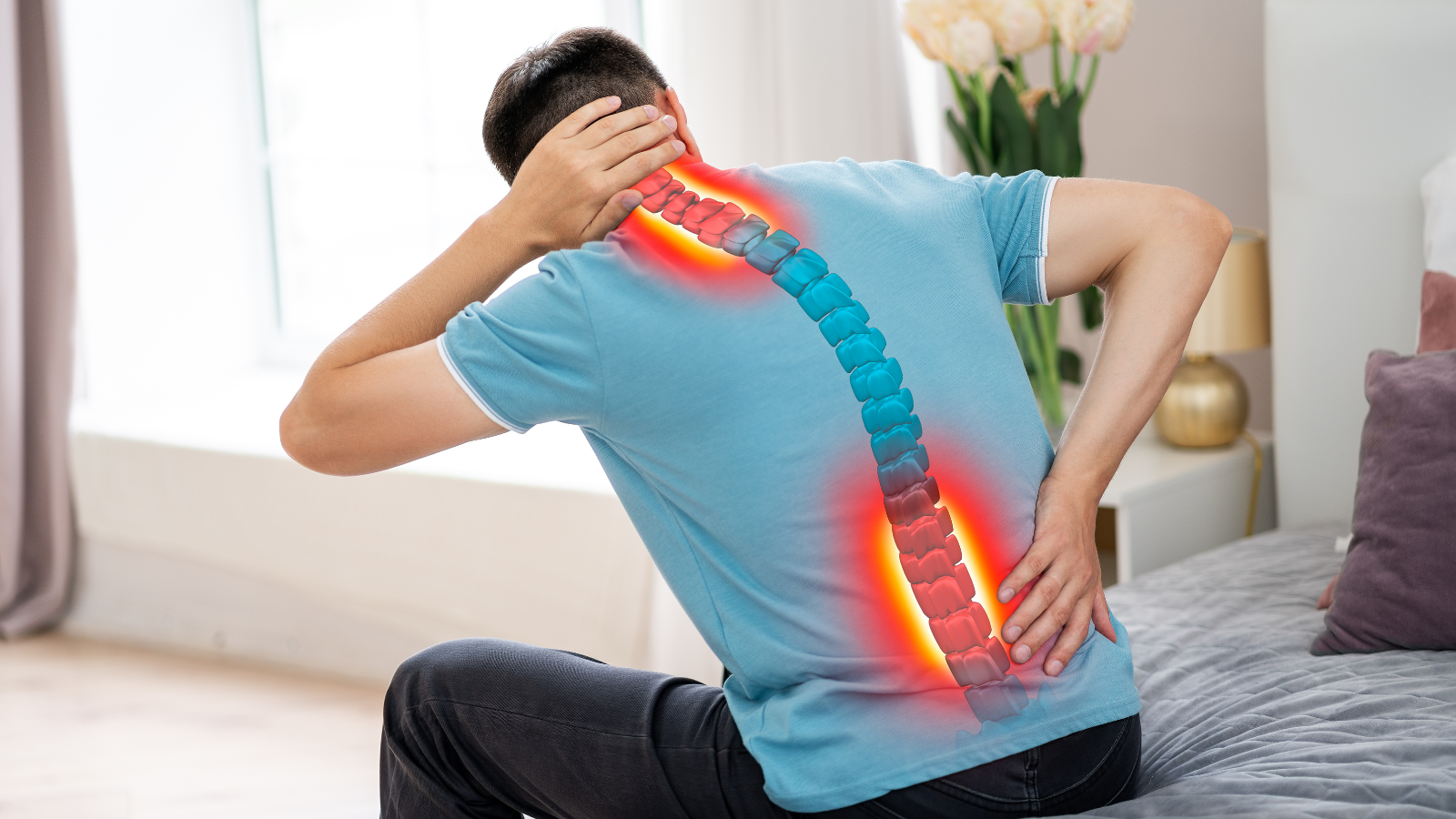
Management strategies for Acute Low back pain
POSTED: 12 Mar, 2024
Acute Low back pain
Back pain is a widespread and often frustrating experience that can impact people across various lifestyles. Understanding the triggers and employing effective management strategies is crucial for overall well-being, particularly when dealing with acute low back pain (LBP) that lasts from a few days to a few weeks.
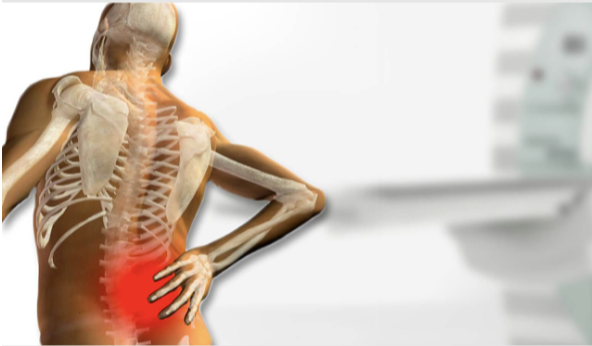
What is Acute Low Back Pain?
Acute LBP arises from irritation or damage to back muscles, nerves, bones, or structures. Its rapid onset requires prompt attention and management to prevent long-term issues.
Common Causes of Acute LBP
Muscle Strains: Overstressed back muscles or ligaments.
Nerve compression: Compression of the sciatic nerve by a herniated disk.
Arthritis: Osteoarthritis affecting spinal ligaments, tendons, and muscles.
Kidney Problems: Issues like kidney stones or infections causing back pain.
Other Disorders: Tumours or spinal-related problems contributing to acute LBP.
Understanding these causes aids individuals in assessing the nature and severity of their back pain, guiding them toward the right course of action.
Initial Treatment Protocol
Rest: Minimize movement without prolonged bed rest.
Icing: Apply ice packs for 20 minutes every hour to manage inflammation.
Avoid HARM in initial days: H: Heat, A: Alcohol, R : Re-injury, M: Massage in first few days. Avoid activities that worsen pain initially.
Medication: Use medications as per your doctor or pharmacist’s advice
Next Steps in Treatment
Physiotherapy: Engage in prescribed exercises to alleviate and prevent LBP recurrence.
Heat Application: Apply heat after the acute phase for muscle relaxation.
Mindfulness Techniques: Meditation and deep breathing for psychological coping.
Preventing Future Incidents
Stay Active and Flexible: Regular exercise, especially focusing on spinal flexibility and core strength, helps ward off LBP.
Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise to reduce pressure on the lower back.
Ergonomics: Ensure an ergonomic workspace to minimize back strain.
These strategies collectively work to manage acute LBP and reduce the likelihood of future episodes.
Thorough Communication
Provide detailed information about your condition for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effectively managing acute LBP involves a multifaceted approach of self-care, medical intervention, and lifestyle adjustments. By staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, adopting ergonomic practices, seeking professional advice, and taking preventive measures, individuals can overcome acute LBP and resume a healthy, active life. The back serves as the body’s structural support; treating it well ensures long-term well-being.
Contact us on 07 3419 4796 today to schedule your appointment.
Reference
https://www.health.qld.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0024/433707/ed-back_pain.pdf
Recent News
-
Knee and ACL Injuries
Knee and ACL Injuries Knee injuries, including anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears, are prevalent in the athletic community, necessitating a proac...
-
Pelvic Girdle Pain in Pregnancy
🌸 Embrace Every Step of Your Pregnancy Journey with Comfort and Confidence! 🌸 Pregnancy is a miraculous chapter in a woman's life, marked by th...
-
Joint Pain in Tradespersons
The Joint Pain in Tradespersons According to the research completed by APA ( Australian Physiotherapy Association), 69% of tradies believe that bein...